School of Liberal Arts February 2025 Newsletter


Student Flexes Media Skills as PA for Super Bowl
Xyy Yang (SLA ’27) applied his Digital Media Practices (DMP) coursework — and experience as a Dean’s Office videographer — to the real world last week, working as production assistant for an NYC sports marketing agency during their Radio Row media coverage preceding Super Bowl LIX.
Experience Awards Season with SLA

Students Immerse Themselves in the Action at Sundance Film Festival
Professor of Practice Jolene Pinder brought 13 students to the biggest independent film fest in the U.S. for a curated Sundance experience with three full days of premieres, panels, and plenty of networking with industry professionals.
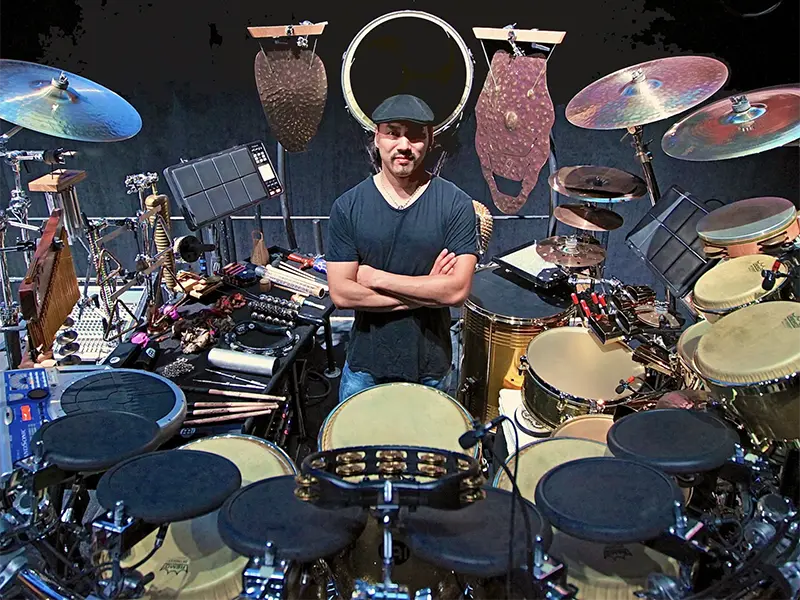

Music Professor Invited to Perform in Special Tribute at 2025 Grammys
After playing in the Quincy Jones tribute on music's biggest stage, Newcomb Department of Music Professor of Practice Taku Hirano shares his thoughts on the industry and how he brings these performances into his teaching.
Literary Lessons
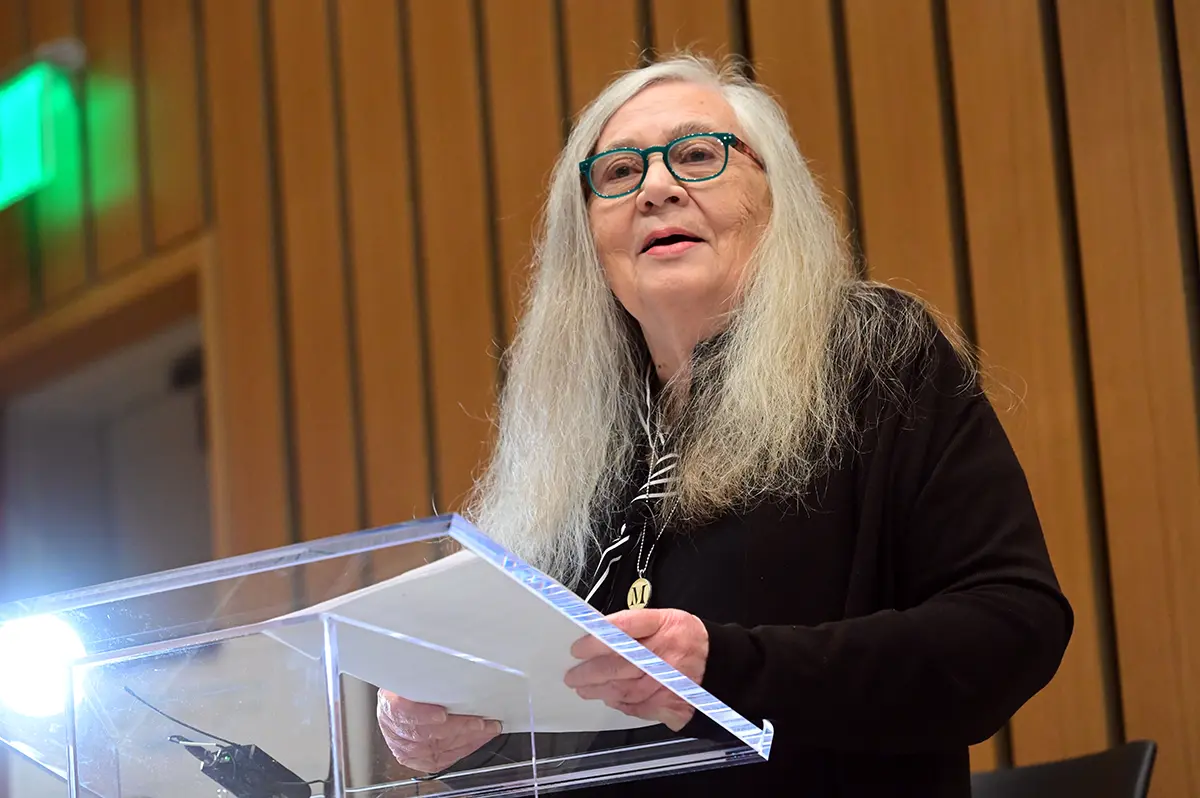

In January, the School of Liberal Arts brought Pulitzer Prize-winning author Marilynne Robinson to Tulane University for the fourth Carole Barnette Boudreaux ‘65 Great Writer's Series, which featured a public talk and book signing, a faculty discussion, and a visit with students.
The Sounds of Mardi Gras
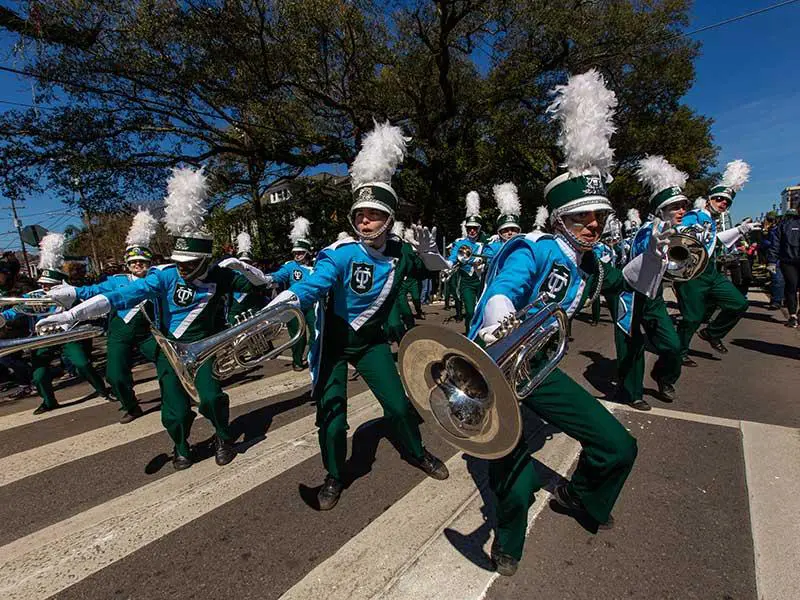

Don’t miss the Tulane University Marching Band (TUMB) — the only collegiate marching band to annually perform in some of the biggest New Orleans Mardi Gras parades — this season!
View Parade Schedule
Featured Event
Young Alumni Perspectives: Navigating Careers with a Liberal Arts Degree
Alumni across industries will visit campus for a discussion around career opportunities for liberal arts graduates. Co-hosted by NTC Career Services and the School of Liberal Arts, this panel of recent SLA grads will share their unique professional paths in speaking to current students. View Panelists
Thursday, March 13, 2025 | 5pm - 7pm | Diboll Gallery

Pulitzer-Winning Novelist Marilynne Robinson Talks “American Beauty” at Great Writers Series
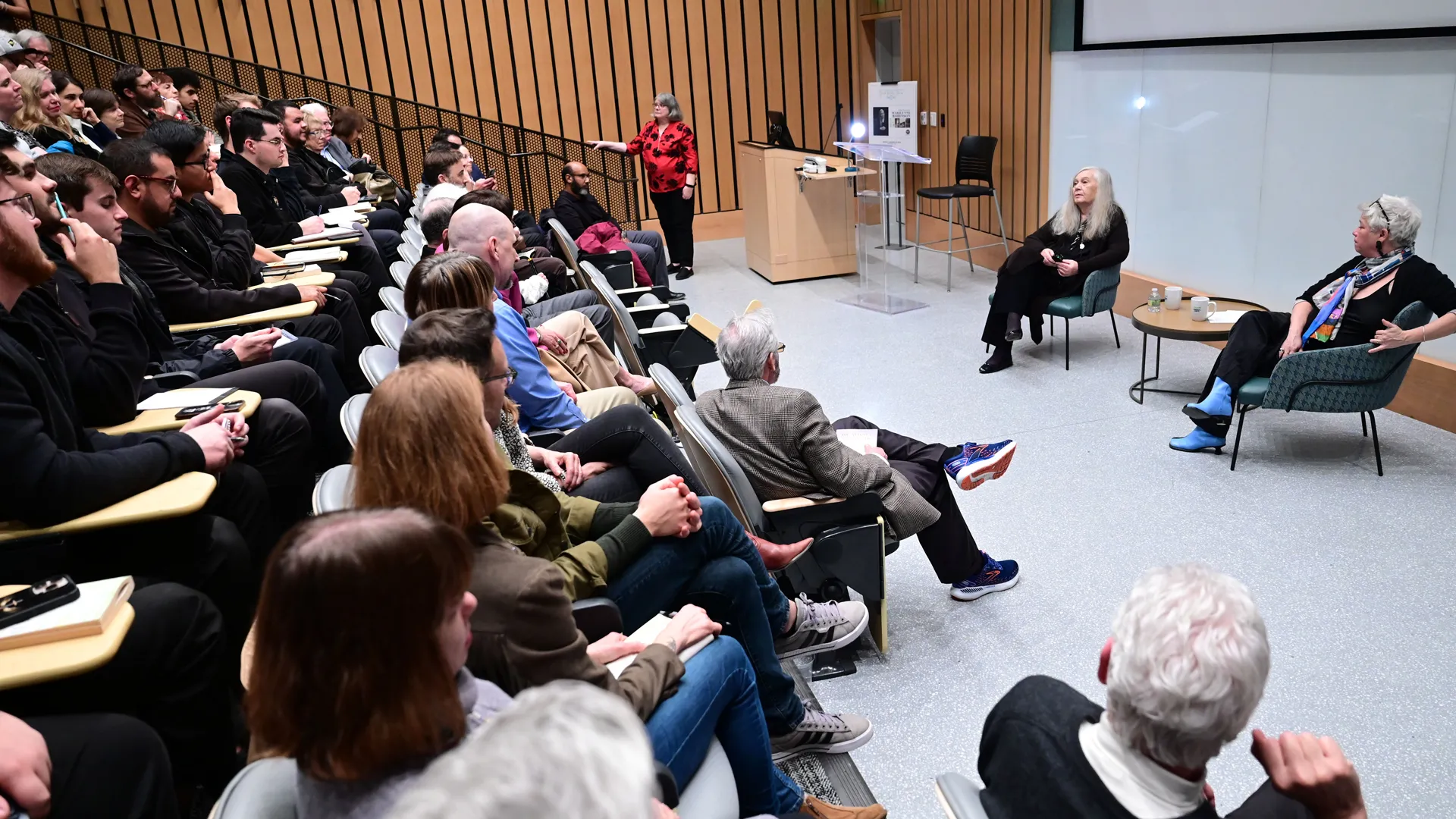 A full room for author Marilynne Robinson, pictured during audience Q&A moderated by Associate Professor of English Karen Zumhagen-Yekplé.
A full room for author Marilynne Robinson, pictured during audience Q&A moderated by Associate Professor of English Karen Zumhagen-Yekplé.
On Tuesday, January 28, 2025, the School of Liberal Arts welcomed Pulitzer Prize-winner Marilynne Robinson as the fourth visiting author in its Carole Barnette Boudreaux ’65 Great Writers Series, where she was greeted by an at-capacity theater on campus for her public talk.
Robinson is the recipient of a 2012 National Humanities Medal, awarded by President Barack Obama, for “her grace and intelligence in writing.” She is the author of Gilead, winner of the 2005 Pulitzer Prize for Fiction and the National Book Critics Circle Award; Home, winner of the Orange Prize and the Los Angeles Times Book Prize; and Lila, winner of the National Book Critics Circle Award.
The annual literary series is supported by the Carole Barnette Boudreaux ’65 Creative Writer Endowed Fund that Tulane alumni Carole B. and Kenneth J. Boudreaux generously gifted in 2018. Barnette Boudreaux received her Bachelor of Arts in English from Newcomb College in 1965 before completing a Master of Education at the University of New Orleans in 1973.
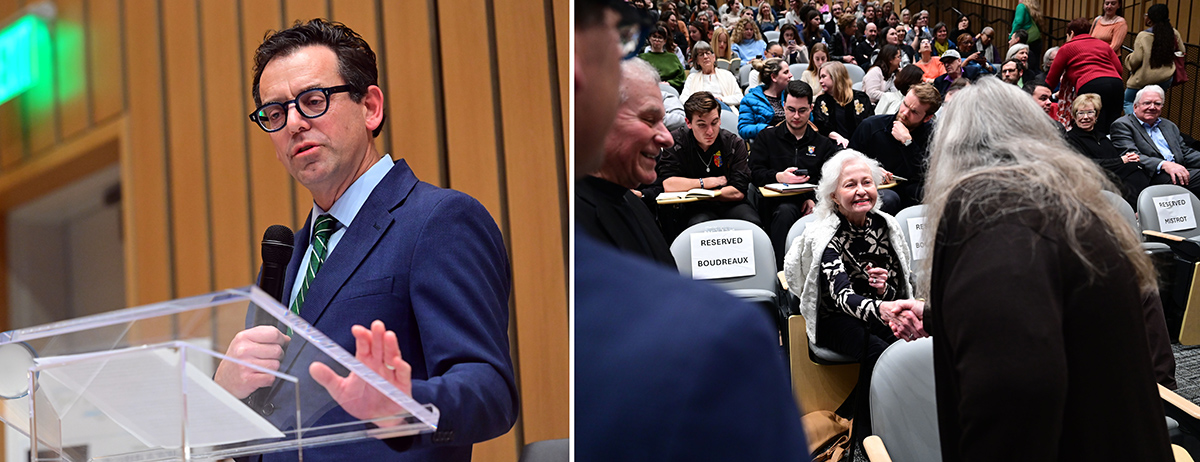 Dean Brian Edwards introduces Robinson; Robinson greets Carole Barnette Boudreaux.
Dean Brian Edwards introduces Robinson; Robinson greets Carole Barnette Boudreaux.
In talking about the breadth of the series, Dean Brian Edwards noted, “The goal is not only to explore the literary work of these authors, but to engage with the ideas they are probing through their own work, from technology and AI to the environmental crisis to political refugees.” Since beginning with Viet Thanh Nguyen in 2021, its programming has continued to grow through collaborations with relevant academic faculty, citywide libraries, and special student interest groups — all intended to augment the keynote lecture and offer further opportunities for Tulanians to engage with the visiting writer.
“Marilynne Robinson is a novelist of exceptional depth and beauty, and a thinker about belief, faith, and the American landscape who has opened so many vistas. Her deep exploration of religion, history, and identity assert the importance of the humanities.”
- Dean Brian T. Edwards
As Robinson took the podium, she announced that she had rewritten the entire essay just days prior — giving a well-received disclaimer that it wasn't very long — in favor of a longer question and answer period, which she admitted she loves. She addressed expected themes like religion and characterization, but also posed questions around hope and AI, suggesting that the only thing that will be lost to efficiency is meaning.
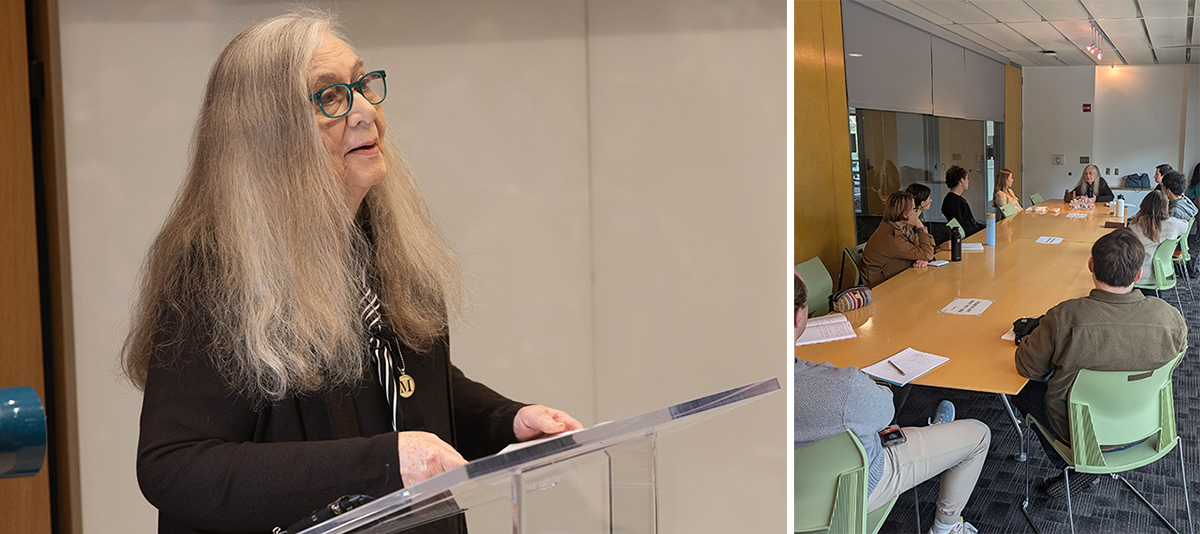 L: Robinson delivers essay in Lake Theater; R: student working group.
L: Robinson delivers essay in Lake Theater; R: student working group.
Her reading ended with a discussion with English Associate Professor Karen Zumhagen-Yekplé, who asked a set of questions tying Robinson’s beliefs with her lifelong activities as a teacher, as a persuasive writer, and as an active citizen.
“My experience of your literary work is that it asks the reader to rise to the occasion of interpretation. Your writing challenges us to think hard [...] and has so much to do with opening our eyes and asking us to think, very often concerned with correcting misreadings and misunderstandings,” said Zumhagen-Yekplé. From there, audience members continued to engage with the author as she took ensuing questions.
Leading up to Robinson’s visit, two faculty & staff reading groups — one focused on Housekeeping and helmed by Professor of English, Communication, and Gender & Sexuality Studies Kate Baldwin, and one addressing Gilead and moderated by Zumhagen-Yekplé — were hosted by the Dean's Office. Attendees were also invited to meet Robinson during a roundtable discussion titled “Faith and Belief in Literature,” led by Michael Kuczynski, Pierce Butler Chair in the Department of English, and Ronna Burger, Catherine & Henry J. Gaisman Chair in the Department of Philosophy.
On the day of her lecture, Robinson had an intimate Q&A with a group of creative writing and literature students — undergraduate and graduate alike — including Leah Starr (SLA '25), who later co-authored a Hullaballoo recap piece of the series with Maya Shields (SLA '26). In their article, the two Tulane journalists close with an impactful quote from classmate Ellie Goodall (SLA '24): "I left Lake Theatre feeling fortunate to be part of an institution full of opportunities to hear from the brightest minds of our time. Marilynne Robinson struck me as a one-of-a-kind intellectual.”
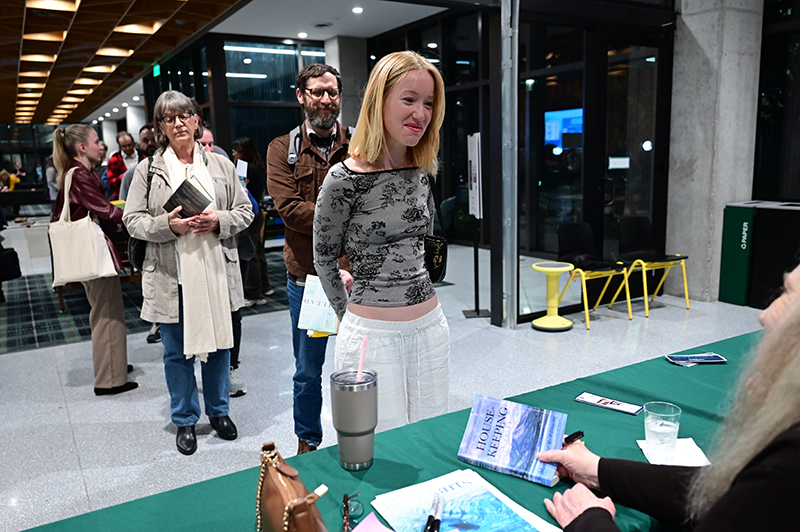

Ellie Goodall (SLA ’24) speaks with Marilynne Robinson as her book is signed.
Tulane Students Take on The Sundance Film Festival
Three days of industry networking, viewing films, and attending panels in Park City create lasting impressions — and valuable connections — for SLA Digital Media Practices (DMP), Communication, and Cinema Studies students.
An opportunity to attend the Sundance Film Festival — the largest independent film festival in the U.S. — is a dream for many creators. This year, DMP collaborated with student-run organizations Green Wave Films (GWF) and Entertainment Business Network (EBN) to take 13 SLA students on a trip to the premier event.
After arriving in Park City, Utah, the students spent three full days watching independent films, attending panels with renowned industry luminaries, and networking with filmmakers and entertainment executives. As part of a curated Sundance experience, the Tulane delegation welcomed Tatiana Bears, co-producer of one of the most buzzed-about films at this year's festival — If I had Legs I’d Kick You from A24 — for an intimate Q+A. Bears shared insight on the complete filmmaking process, from developing and financing a film, to taking it to a premier showcase like Sundance.
“Attending the 2025 Sundance Film Festival was nothing short of transformative,” said Kristine Liang, DMP coordinate major. “Sundance revitalized my purpose as an aspiring filmmaker, showing me how much space there now is for stories like mine. One of the most profound moments was attending the world premiere of BUNNYLOVR, starring the wildly impressive writer/director, Katarina Zhu. I felt that her fearless exploration of sexual shame, internalized racism, and the complexities of Asian-American identity were breathtaking.”
The trip was led by DMP and Communication Professor of Practice Jolene Pinder, Professor of Practice Duane Prefume, and Adjunct Professor Bo McGuire. Pinder is a Sundance | Adobe Women to Watch Fellow this year; an installation, featuring clips of Pinder’s recently produced short film, was available for viewing at the Adobe House on Main Street during the festival. She, along with a few of the students, were able to do a walk-through of the house to see the installation and meet with Andrea Gutierrez from Adobe. During that conversation, Gutierrez encouraged the students to apply for the Sundance Ignite x Adobe Fellowship for filmmakers aged 18-25 — creating a fantastic networking opportunity they can draw upon in the future.

During his time in Park City, DMP coordinate major and GWF co-founder Noah Levine was able to make steps towards securing a post-grad assistant job in LA. “Going to this year’s festival helped me tremendously both in networking and seeing what this industry is all about firsthand,” he shared. “I was able to meet and connect with individuals from companies I’m very interested in, like Netflix and Paramount. This would not have been possible if I had not been at the festival! Sundance was an incredible experience and helped move my career forward.”
“Sundance offered us a rare glimpse into the world of filmmaking that we had yet to see” shared Olive Wheadon, DMP coordinator major and president of EBN. “We left with an even stronger connection to the craft, enriched by the stories, insights, and energy that surrounded us.”
For DMP coordinate major Mackenzie Camp, a chance encounter with a producer waiting in line for the same movie landed her a job interview with Range Media Partners.
Liang concluded, “It’s the ability of even the most niche and esoteric stories to foster compassion and evoke resonance that drives me as a filmmaker. The energy in those theaters felt incredibly rare — resembling that of an unbreakable community rooted in courage and passion. It was everything I love about film — everything I hope to create myself one day. I am endlessly grateful for the opportunity to have been part of it.”
Of his experience on the trip, DMP coordinate major and GWF Production Chair Julian Hewitt added, "As a student filmmaker, the most you can ask for from any university is an opportunity to be exposed to the film industry. Leaving Tulane with a trip to Sundance was not only a perfect ending to my time as a student filmmaker but ended up being one of the best weekends of my life. To walk around with professionals so casually felt extremely natural and made me confident to take my next step into the industry."
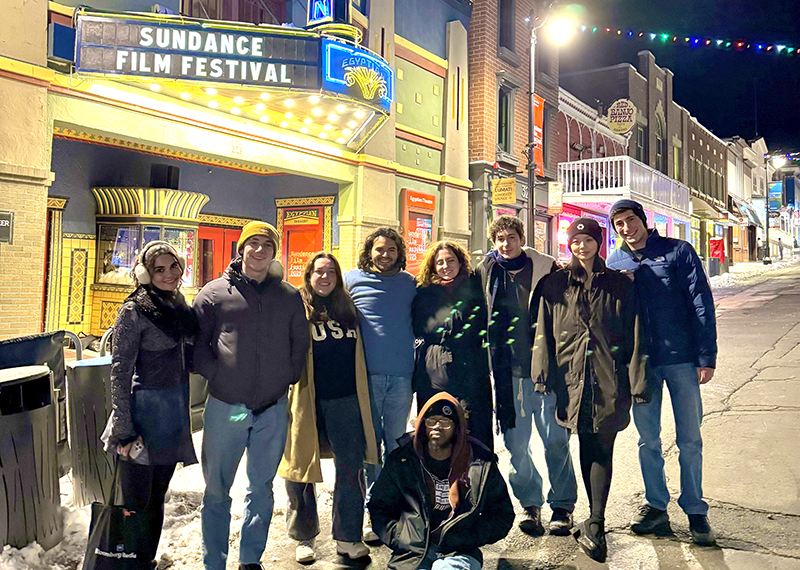

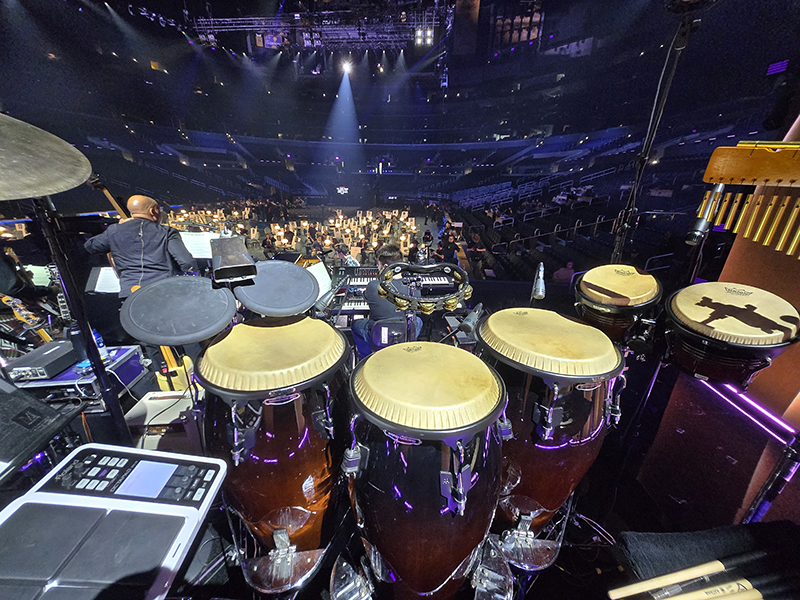
Tulane Music Professor plays Quincy Jones Tribute at the 2025 Grammy Awards

Third from left, Taku Hirano provides musical accompaniment as Lainey Wilson performs during the Quincy Jones Tribute at the 2025 Grammy Awards. Photo Courtesy of CBS via The Recording Academy/Grammys.
As one of the industry’s most in-demand percussionists, Taku Hirano is no stranger to sharing the big stage with musical greats like Stevie Wonder, Fleetwood Mac, and Whitney Houston. Most recently, the Newcomb Department of Music Professor of Practice in Music Industry Studies was invited to join the 2025 Grammy award show as part of a star-studded tribute to industry legend Quincy Jones, backing Herbie Hancock, Stevie Wonder, Cynthia Erivo, Lainey Wilson, Jacob Collier, and Janelle Monaé. The invitation for this prestigious honor was extended to him by Greg Phillinganes — former session keyboardist for many of Quincy Jones’ seminal recordings and musical director for Michael Jackson’s world tours.
Hirano met Phillinganes while touring the world for two years on Michael Jackson: THE IMMORTAL World Tour — a joint production by Cirque du Soleil and the Michael Jackson Estate — and has also worked with the musician and director on previous Grammy Awards telecasts, including a tribute to Motown Records founder Berry Gordy in 2023 (where they performed behind Stevie Wonder, Smokey Robinson, and Chris Stapleton), a musical tribute to Lionel Richie in 2016 (where they performed with John Legend, Demi Lovato, Meghan Trainor, Luke Bryan, Tyrese, and Lionel Richie), as well as the All-Star Grammy Salute to Stevie Wonder special on CBS (backing Beyoncé, Lady Gaga, Ariana Grande, Ed Sheeran, John Legend, Janelle Monaé, Gary Clark, Jr., Pharrell, Ne-Yo, Annie Lennox, Babyface, and Andrea Bocelli). At Tulane, Hirano applies his invaluable professional knowledge to teaching courses in Music Industry Studies within the Newcomb Department of Music and the Strategy, Leadership, Analytics Minor (SLAM), working with students to shape their own musical careers — and the future of the industry.
He shares his thoughts around the Grammy experience, technology and music, and how he incorporates performances like these into his teaching.
What was your favorite part of the experience?
My favorite part of this latest Grammy Awards performance was reuniting and catching up with longtime and fellow musician-friends. Within the Quincy Jones tribute band, there were friends I hadn’t seen since the Grammys two years ago.
It has always been a dream of mine to be able to take my musical training and apply it to thrilling experiences, backing artists on the largest of stages and on tours around the world. For this year’s Grammys, being in the room and part of the creative process, working out arrangements alongside Herbie Hancock, Stevie Wonder, Cynthia Erivo, Jacob Collier, and Lainey Wilson in rehearsals was a fun, unique experience — and I don’t take it for granted. It is a thrill that few get to experience.
What did you bring back to the classroom from this experience?
Upon returning to class, I was able to share with my Intro to Music Business (MUSC2800) and Intro to Creative Industries (SLAM2600) classes photos and videos from behind-the-scenes and explain the logistics that went into rehearsals, camera-blocking, dress rehearsals, and the live performance that was seen by 15.4 million people. Also, it came to my attention that I had some students hold a viewing party! It warmed my heart to hear that my students and colleagues were thrilled for me and tuned in.
Which musicians inspired your career?
There are a myriad of musicians who have inspired me. One of my mentors was legendary session drummer Ndugu Chancler, who coincidentally worked a lot with Quincy Jones. Ndugu was one of the drummers on Michael Jackson’s Thriller album, playing drums on the hit song “Billie Jean.” He also worked with Quincy Jones on the film The Color Purple and even appeared in the movie. Ndugu played an instrumental part in both my education as well as introducing me to the music scene once I arrived in Los Angeles upon finishing my undergraduate studies.
Who's playing on your Spotify?
I currently have been listening to New Orleans legends The Meters. Not only are they one of my favorite groups, but they were also founded by my late father-in-law, Art Neville — who also went on to lead the Grammy-winning group, The Neville Brothers.
What are you most excited about for the future of music?
I am interested in seeing the integration of technology and AI with music, and its implications on copyright, rights management, and intellectual property issues. As a graduate student, my main area of focus was copyright, licensing, and metadata as it relates to music, as well as music supervision (the synchronization licensing of music for use in other forms of media such as film, TV, gaming, and advertising). We are in the middle of a very consequential period of how technology is intersecting with the music industry, and I have been keeping a close eye on it.


More about Taku Hirano:
Other notable performances Hirano has performed under the direction of Phillinganes include Women of Soul: In Performance at the White House for the Obama Administration (backing Patti LaBelle, Melissa Etheridge, Ariana Grande, Jill Scott, and Janelle Monaé); Imagine: John Lennon 75th Birthday Concert at Madison Square Garden (backing Willie Nelson, Kris Kristofferson, Steven Tyler, Sheryl Crow, Peter Frampton, John Fogerty, Chris Stapleton, Eric Church, Aloe Blacc, and Tom Morello); and Oprah’s Farewell Spectacular (backing Aretha Franklin, Stevie Wonder, Patti LaBelle, Usher, Jamie Foxx, Josh Groban, and Kristin Chenoweth).
Hirano first performed at the Grammy Awards with the Backstreet Boys back in 2000, and has also performed on the American Music Awards with Lil Wayne and Fleetwood Mac; the Soul Train Awards with Whitney Houston and Chaka Khan; the BET Honors with Aretha Franklin, Smokey Robinson, Jennifer Hudson, and Janelle Monaé; and the Grio Awards with Patti LaBelle, Jennifer Hudson, Yolanda Adams, and Queen Latifah.




